Say you have an array prices for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete as many transactions as you like (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock multiple times).
Note: You may not engage in multiple transactions at the same time (i.e., you must sell the stock before you buy again).
Example 1:
Input: [7,1,5,3,6,4] Output: 7 Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 3 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4. Then buy on day 4 (price = 3) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-3 = 3.
Example 2:
Input: [1,2,3,4,5] Output: 4 Explanation: Buy on day 1 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4. Note that you cannot buy on day 1, buy on day 2 and sell them later, as you are engaging multiple transactions at the same time. You must sell before buying again.
Example 3:
Input: [7,6,4,3,1] Output: 0 Explanation: In this case, no transaction is done, i.e. max profit = 0.
Constraints:
- 1 <= prices.length <= 3 * 10 ^ 4
- 0 <= prices[i] <= 10 ^ 4
문제 풀이:
만약 배열이 [7,1,5,3,6,4]라고 해보자
1에 사고 6에 팔아도 되지 않을까?라고 생각하지만 그게 최댓값은 아니다.
아래 그림을 살펴보자.
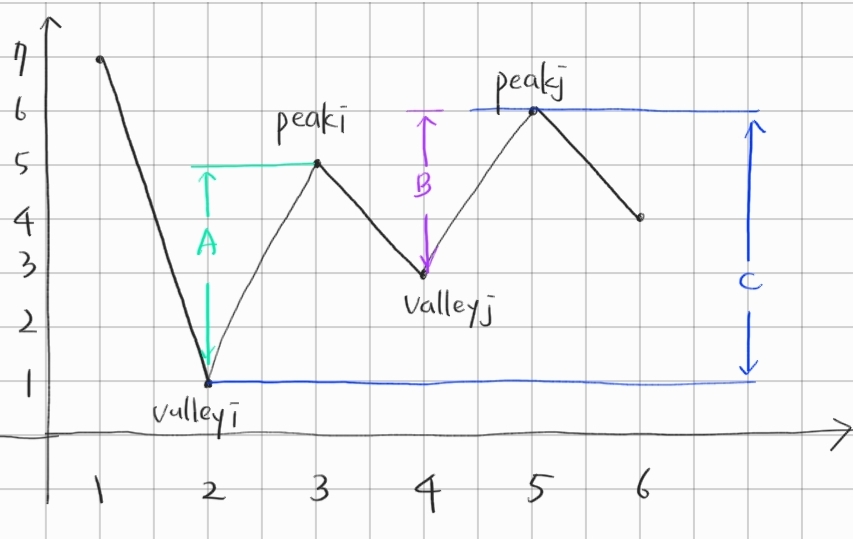
peak valley approach
물건을 팔기 위해선 valley후에 peak이 나와야한다. prices[i] < prices[i+1]
이 때 항상 A+B >= C 즉, 부분 차이들의 합은 전체 차이보다 크거나 같다는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
따라서 매번 차이만큼 더해줘야 한다.
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int max = 0;
for(int i=1; i<prices.length; i++){
if(prices[i] > prices[i-1]){
max += prices[i] - prices[i-1];
}
}
return max;
}
}'알고리즘 문제풀이 > leetcode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [leetcode 107] Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II (0) | 2020.11.21 |
|---|---|
| [leetcode 108] Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree (0) | 2020.11.20 |
| [leetcode 125] Valid Palindrome (0) | 2020.11.20 |
| [leetcode 118] Pascal's Triangle (0) | 2020.11.19 |
| [leetcode 66] Plus One (0) | 2020.11.19 |



댓글