1. Spring Bean이란?
- 자바 스프링에서 POJO(plain old java object)를 가리키는 용어
- 어플리케이션의 핵심을 이루는 객체
- spring IoC(Inversion of Control)에 의해 인스턴스화, 관리, 생성된다.
- xml에서 생성된다.
2. Bean Component
1) class (필수)
2) id : bean 고유 식별자
3) scope: 객체의 범위
4) constructor-org: 생성 시 생성자에 전달할 인수
5) property: 생성 시 bean setter에 전달할 인수
6) init/destroy method
3. Bean Scope란?
- 모든 bean의 디폴트는 singleton
- request, session, global session은 Spring MVC Web Application에서만 사용된다.

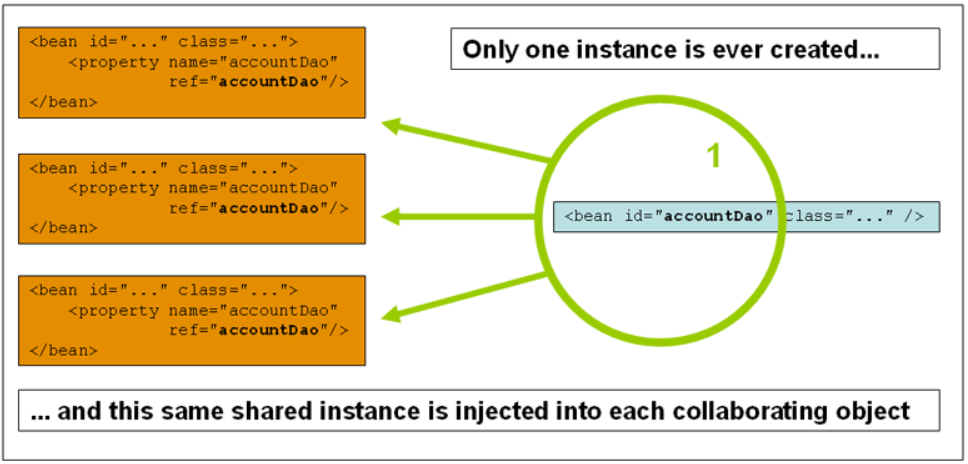
1) singleton
- 컨테이너에서 한 번 생성된다. -> 컨테이너가 사라지면 bean도 제거
- 생성된 하나의 인스턴스는 캐시에 저장되어 사용된다. 어차피 하나기 때문에 동일한 것을 참조
- 모든 bean은 디폴트로 singleton이다.
- 자바 메인클래스에서 호출 시 여러번 불러도 모두 동일한 메모리 주소를 가리킨다.
- xml 설정
<bean id="..." class ="..." scope="singleton"> </bean>
- annotation 설정
@Scope("singleton")
2) prototype
- 모든 요청에 대해 새로운 객체를 생성하는 것을 의미한다.
- 하나의 bean정의에 대해 다수의 객체가 존재가능하다.
- 자바 메인 클래스에서 호출할 때마다 다른 메모리 주소를 가리킨다.
- init 메소드는 정의가능하지만 destroy 메소드는 정의 불가능하다.
//retrieve bean from spring container
Coach theCoach = context.getBean("tennisCoach", Coach.class);
Coach alphaCoach = context.getBean("tennisCoach", Coach.class);
//check if they are the same
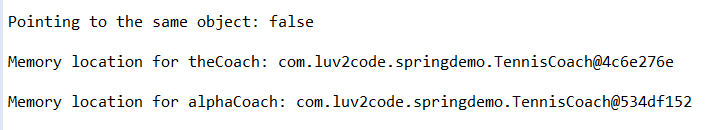
boolean result = (theCoach==alphaCoach);
System.out.println("\\\\nPointing to the same object: " + result);
System.out.println("\\\\nMemory location for theCoach: "+ theCoach);
System.out.println("\\\\nMemory location for alphaCoach: "+ alphaCoach);
결과:
- gc에 의해 bean이 제거된다.
- xml 설정
<bean id="..." class ="..." scope="prototype"> </bean>
- annotation 설정
@Scope("prototype")
cf)
- 싱글톤으로 적합한 객체
- 상태가 없는 공유 객체
- 읽기용으로만 상태를 가진 공유 객체
- 공유가 필요한 상태를 지닌 공유 객체
- 쓰기가 가능한 상태를 지니면서도 사용빈도가 매우 높은 객체
- 아닌 객체
- 쓰기가 가능한 상태를 지닌 객체
- 상태가 노출되지 않은 객체
4. Injection
1) constructor injection
<bean id="myCoach" class="com.luv2code.springdemo.TrackCoach">
<!-- set up constructor injection -->
<constructor-arg ref="myFortuneService" />
</bean>
2) setter injection + field injection
<bean id="myCricketCoach" class="com.luv2code.springdemo.CricketCoach">
<!-- set up setter injection -->
<property name="fortuneService" ref="myFortuneService"/>
<!-- inject literal values -->
<property name="emailAddress" value="${foo.email}"/>
<property name="team" value="${foo.team}"/>
</bean>
5. Bean의 생성
1. xml configuration
- java를 이용한 context설정이 나오기전 사용하던 방법
- applicationContext.xml이라는 파일을 src/main/resources에 추가시킨 후 bean에 등록한다.
1) xml파일을 만들고 class를 연동
applicationContext.xml
<bean id="myLoggerConfig" class="com.luv2code.springdemo.MyLoggerConfig" init-method="initLogger">
<property name="rootLoggerLevel" value="FINE"/>
<property name="printedLoggerLevel" value="FINE"/>
</bean>
2) main class에서 xml config file을 가져온다.
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 객체를 생성
// 1. load the spring configuration file
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 2. retrieve bean form spring container
Coach theCoach = context.getBean("myCoach", Coach.class);
//3. call out method3) id와 class를 지정해서 xml에 선언된 bean을 부른다. (Retrive bean from spring container)
2. Java configuration
- @configuration이라는 annotation을 사용
- xml 대신 java로 bean을 생성- config class를 만들어서 @Configuration을 달면 끝- bean으로 사용할 객체를 반환하는 메소드를 만들어서 @Bean을 단다.
3. @ComponentScan
- @Configuration과 @ComponentScan을 같이 등록하면 xml없이도 1과 같이 사용가능- @Autowired를 통해 의존성 주입 가능
gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/12/18/spring-annotation-enable.html
'개발 > java spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [java spring] JDBC와 JPA/Hibernate, Mybatis (0) | 2020.09.24 |
|---|---|
| [java spring] maven 이란 (0) | 2020.09.22 |

댓글