The thief has found himself a new place for his thievery again. There is only one entrance to this area, called the "root." Besides the root, each house has one and only one parent house. After a tour, the smart thief realized that "all houses in this place forms a binary tree". It will automatically contact the police if two directly-linked houses were broken into on the same night.
Determine the maximum amount of money the thief can rob tonight without alerting the police.
도둑이 보석을 훔칠 때 무조건 한 개 이상의 노드를 건너 뛰어야 가능하다.
Example 1:
Input: [3,2,3,null,3,null,1] Output: 7

Explanation: Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 3 + 3 + 1 = 7.
Example 2:
Input: [3,4,5,1,3,null,1] Output: 9
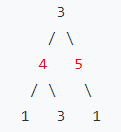
Explanation: Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 4 + 5 = 9.
문제 풀이:
1. 재귀함수를 사용
top down방식으로 재귀함수를 사용하여 값을 구할 수 있다.
주어진 조건: 이진 트리
재귀 함수 구현:
1) 종료 조건: 노드가 nullptr일 때(마지막 리프까지 내려갔을 때) 0값을 더한다.
2) 리턴값은 길이 2짜리 배열. 현재 노드에서 훔쳤을 경우 값은 0 인덱스에, 현재 노드에서 훔치지 않았을 경우 값은 1 인덱스어 넣는다.
3) 현재 노드에서 훔친 값은 어떻게 구하는가? 현재 노드 값 + 이전 노드에서 훔치지 않음(좌, 우 모두)
4) 현재 노드에서 훔치지 않은 값은? 현재에서 훔치지 않으므로 전 노드에서 뭘 하든 딱히 상관없다. 따라서 좌우 각각에서 이전노드에서 훔쳤다 vs 훔치지 않았다의 최대값을 가져온다.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxMoney = 0;
vector<int> recurs(TreeNode *cur){
if(!cur){
return {0,0};
}
vector<int> left(2,0);
left = recurs(cur->left);
vector<int> right(2,0);
right = recurs(cur->right);
int rob = cur -> val + left[1] + right[1];
int notRob = max(left[1], left[0]) + max(right[0], right[1]);
return {rob, notRob};
}
int rob(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root){
return 0;
}
vector<int> answer(2,0);
answer = recurs(root);
return max(answer[0], answer[1]);
}
};
2. dynamic programming
'알고리즘 문제풀이 > leetcode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [leetcode 240] Search a 2D Matrix II (0) | 2020.10.20 |
|---|---|
| [leetcode 287] Find the Duplicate Number (0) | 2020.10.20 |
| [leetcode 437] Path Sum III (0) | 2020.10.18 |
| [leetcode 394] Decode String (0) | 2020.10.18 |
| [leetcode 347] Top K Frequent Elements (0) | 2020.10.18 |

댓글